A new solution to control powdery mildew, downy mildew, gray mold and anthracnose
Azoxy Bio fungicide, a combination of Reynoutria japonica Hout medicinal plant extract and Azoxystrobin fungicide
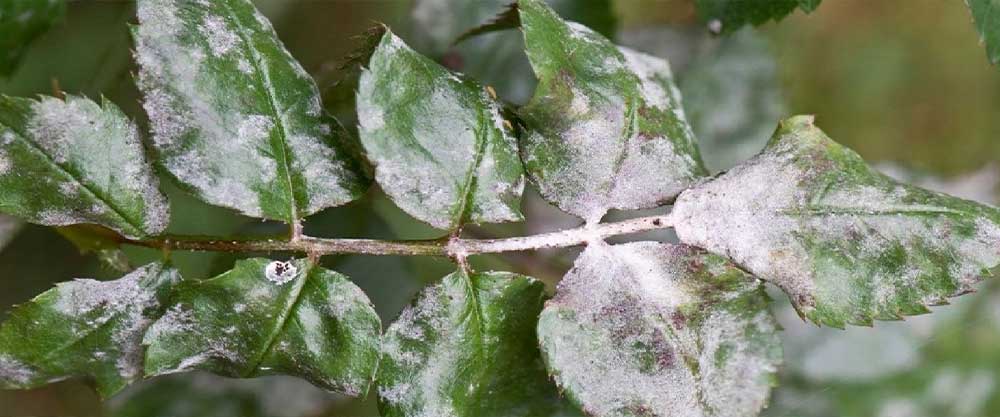
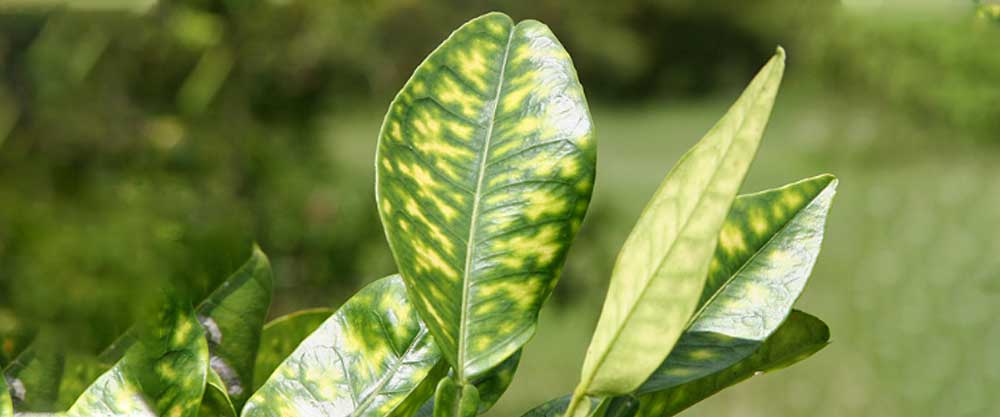
Fungal diseases account for 70-80% of plant diseases. Among the fungal diseases, Botrytis cinereal is one of the main pathogens that can damage more than 470 plants such as Solanaceae, Cucurbitaceae, and Rosaceae [and causes plant leaves to fall, fruits and vegetables to rot, and reduce the quality of agricultural products. to be This disease causes economic losses of more than 10 billion dollars worldwide every year. This important disease in tomato cultivation can reduce the yield of tomatoes by 20-30% and even up to 50%. Among ornamental plants, rose causes more than 70% of post-harvest losses. Fusarium blight disease of wheat spike causes a decrease in grain weight, low germination speed and power, low flour production and quality, and low economic value. In greenhouse environments, hot and high humidity makes it more difficult to control fungal diseases. In China, powdery mildew causes annual strawberry production to decline by 10-20%, and in the case of an outbreak, it can reach more than 50% or even 100%.
For a long time, the control of plant fungal diseases mainly relies on chemical fungicides such as difenoconazole, mycobutanil, tebuconazole, triflumizole, pyraclostrobin, mancozeb, fluazinam, triadimone, pyrimethanil, procymidone, iprodione, etc., which are widely used. take For the control of fungal diseases of crops, preventive and protective fungicides such as mancozeb have limited control effects and when used alone cannot meet the needs of growers for disease control.
Systemic fungicides such as difenoconazole not only inhibit the infection of pathogenic fungi, but also affect the physiological indicators of crops, e.g. Inhibiting chlorophyll synthesis and plant growth and reducing plant resistance against pathogenic fungi. At the same time, the continuous use of chemical fungicides has brought more problems such as resistance, chemical residues and environmental pollution.
According to market research, the global fungicide market continues to develop in recent years. Due to the increasing resistance of pathogenic fungi to chemical fungicides year by year, the market has a continuous demand for new products. According to reports, in 2012 to 2013, Botrytis cinerea plant resistance to carbendazim increased by 63.6% in Hubei Province, China.
Botrytis cinerea resistance to carbendazim increased by 53.6%-99.0% in Liaoning, Hebei, Beijing, Anhui and Sichuan provinces. On the other hand, adjustment of the global structure of crop planting, increase in the area and variety of vegetables, fruits and various economic crops will increase the demand for fungicide products, so fungicides have great potential in the market in the future.
At the same time, with the increase of people's concern about environmental issues and the gradual increase in the field of organic agriculture, the demand for natural product protection inputs with low toxicity and low resistance in the global market will increase. It is necessary to develop a biopesticide that is environmentally friendly, highly efficient, low toxicity, not easy to develop resistance, and can increase crop growth.
Reynoutria japonica Houtt. It is a traditional Chinese medicinal plant found in eastern China, central and southern China, Liaoning, Shanxi, Gansu, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan. According to the traditions of traditional Chinese medicine, its roots and rhizomes are used in medicine, whose effects are to activate blood and relieve pain, remove heat and humidity, remove thirst and phlegm.
Studies have shown that Reynoutria japonica Houtt. It is rich in effective ingredients such as polydatin, resveratrol, emodin and fision. Its extract has an anti-cancer effect with a significant inhibitory effect on the proliferation of tumor cells and can greatly slow down the growth of tumor tissue. At the same time, the secondary metabolites of Reynoutria japonica Houtt have natural resistance to diseases and pests, so very few diseases and pests occur during the growth of Reynoutria japonica Houtt and almost no pest control is required.
Based on the characteristics of secondary metabolites of Reynoutria japonica Houtt and their pharmacological effects, Reynoutria japonica Houtt is used to control plant diseases in agriculture. Fission, as one of the most abundant active substances among the secondary metabolites of Reynoutria japonica Houtt, has high activity against plant diseases such as powdery mildew, downy mildew, gray mold and anthracnose.
Now a division of Prime Source Albaugh, LLC has introduced the fungicide Azoxy Bio (Azoxystrobin and Reynoutria sachalinensis extract), which was registered with the US Environmental Protection Agency in spring 2022. This systemic fungicide can not only prevent and control major diseases in grass and ornamentals, but also strengthens the plant's immune system and achieves good disease resistance management.
With experimental tests, 0.4% Reynoutria japonica Houtt extract had significant inhibitory and destructive effects on powdery mildew spore germination. After 96 hours of treatment, through trypan blue staining and morphological observation, a large number of sporangia were stained with degraded structure and lost germination power.
According to the experiments, it was shown that 0.4% extract of Reynoutria japonica Houtt not only had excellent control effectiveness, but also promoted crop growth and reduced pesticide stress on crop growth. With the recommended concentration, the length and width of the leaf is 1.26 respectively