Encouraging news about the complete management of citrus greening disease
American Agricultural Research Service (ARS) scientists may have found a potential cure for an incurable disease that has ravaged the U.S. citrus industry since it arrived in Florida in 1998.
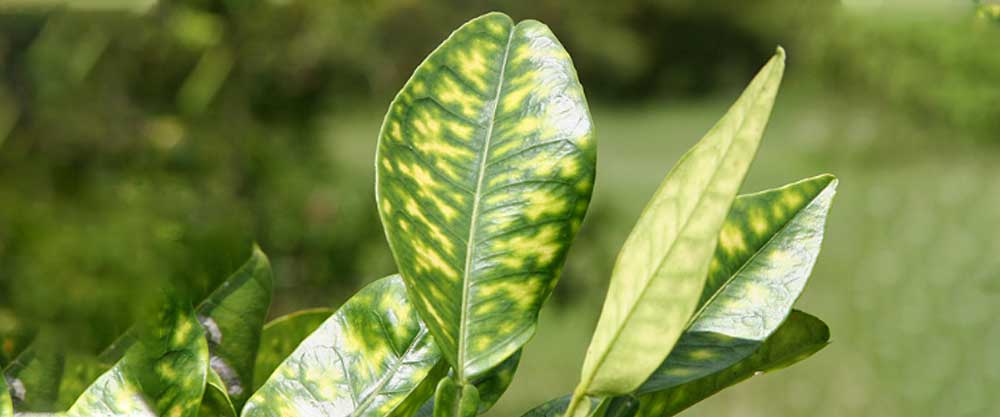
Huanglongbing (HLB), also known as citrus greening, is a disease that infects citrus trees in a way that renders the fruit unusable and slowly kills the tree. Since 2005, HLB has spread throughout Florida, destroying countless trees and orchards, reducing citrus production by 75 percent, and more than doubling production costs. The disease has now made its way west through Louisiana, Texas, and into California. The disease is spread by the Asian citrus psyllid (ACP), a small sap-sucking insect that carries Candidatus liberibacter asiaticus (CLas), the bacterium that causes HLB. The psyllids transmit the disease by injecting bacteria-filled saliva into the tree while feeding. After that, there is no hope for the tree.
Researchers at the ARS Plant Breeding and Genetics Research Unit (CIGR) in California have discovered a way to increase a tree's natural resistance to pathogens, including HLB, by combining receptors that can recognize pathogens and trigger innate immune responses. activated the plant.
At first, the main challenges of operationalizing this approach were identifying suitable genes capable of detecting HLB, sufficient combination of genes to be effective, and designing a path for their entry into the gene structure of the tree. One of the ways of gene transfer is the use of agrobacteria that originate from the soil. These bacteria are a type of plant engineering tool where you add the cloned DNA you want from plants with natural resistance to the pathogen of concern, and then the agrobacteria add that specific piece of DNA to the plant genome. "
The next step is to get the DNA and load it into the target trees. This is done in the laboratory through tissue culture. Some of the original plant is cut into small pieces and temporarily mixed with agrobacteria. Then, the pieces of the plant, free of agrobacteria, turn into a whole plant again."

Asian citrus psyllid feeds on citrus stems
Before, there was no cure for the affected tree. The only practical way to deal with HLB was to remove affected trees from orchards and chemically control HLB vector psyllium and cover the trees in tents. In case of using cultivated seedlings with the feature of inherent defense system capability, compared to greening, the economic profit will be at least three times for the farmers. Undoubtedly, this HLB-fighting technology will be used in the next few years. Currently, a series of genes that activate plant defense responses in the presence of HLB and can recognize and combat HLB have been identified.